One of my holiday projects was to understand and gain more trust in how Debian binaries are built, and as the holidays are coming to an end, I’d like to introduce a new research project called Debian Taco. I apparently need more holidays, because there are still more work to be done here, so at the end I’ll summarize some pending work.
Debian Taco, or TacOS, is a GitSecDevOps rebuild of Debian GNU/Linux.
The Debian Taco project publish rebuilt binary packages, package repository metadata (InRelease, Packages, etc), container images, cloud images and live images.
All packages are built from pristine source packages in the Debian archive. Debian Taco does not modify any Debian source code nor add or remove any packages found in Debian.
No servers are involved! Everything is built in GitLab pipelines and results are published through modern GitDevOps mechanism like GitLab Pages and S3 object storage. You can fork the individual projects below on GitLab.com and you will have your own Debian-derived OS available for tweaking. (Of course, at some level, servers are always involved, so this claim is a bit of hyperbole.)
Goals
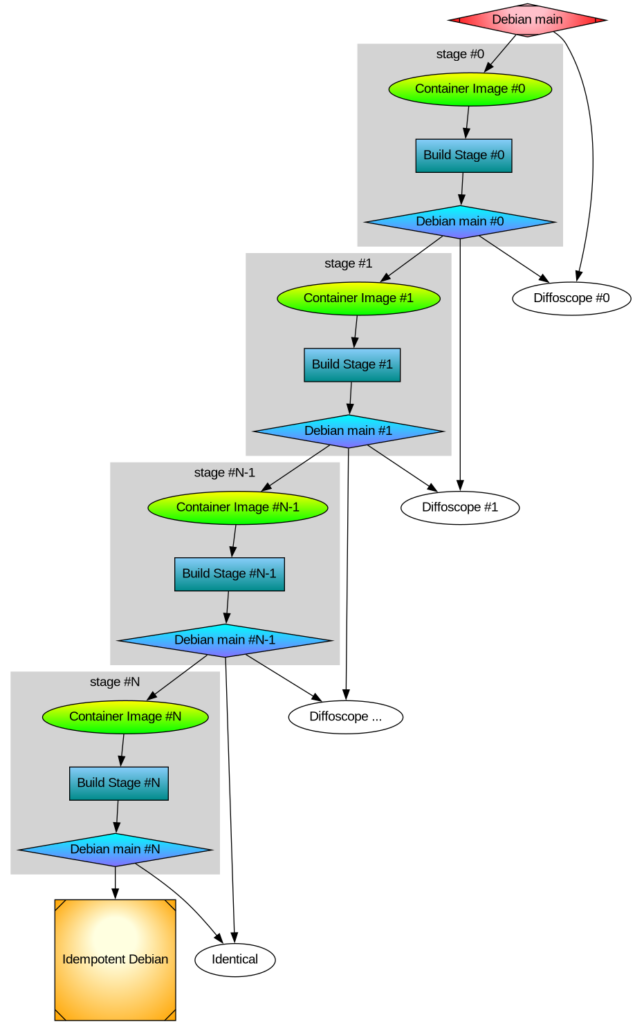
The goal of TacOS is to be bit-by-bit identical with official Debian GNU/Linux, and until that has been completed, publish diffoscope output with differences.
The idea is to further categorize all artifact differences into one of the following categories:
1) An obvious bug in Debian. For example, if a package does not build reproducible.
2) An obvious bug in TacOS. For example, if our build environment does not manage to build a package.
3) Something else. This would be input for further research and consideration. This category also include things where it isn’t obvious if it is a bug in Debian or in TacOS. Known examples:
3A) Packages in TacOS are rebuilt the latest available source code, not the (potentially) older package that were used to build the Debian packages. This could lead to differences in the packages. These differences may be useful to analyze to identify supply-chain attacks. See some discussion about idempotent rebuilds.
Our packages are all built from source code, unless we have not yet managed to build something. In the latter situation, Debian Taco falls back and uses the official Debian artifact. This allows an incremental publication of Debian Taco that still is 100% complete without requiring that everything is rebuilt instantly. The goal is that everything should be rebuilt, and until that has been completed, publish a list of artifacts that we use verbatim from Debian.
Debian Taco Archive
The Debian Taco Archive project generate and publish the package archive (dists/tacos-trixie/InRelease, dists/tacos-trixie/main/binary-amd64/Packages.gz, pool/* etc), similar to what is published at https://deb.debian.org/debian/.
The output of the Debian Taco Archive is available from https://debdistutils.gitlab.io/tacos/archive/.
Debian Taco Container Images
The Debian Taco Container Images project provide container images of Debian Taco for trixie, forky and sid on the amd64, arm64, ppc64el and riscv64 architectures.
These images allow quick and simple use of Debian Taco interactively, but makes it easy to deploy for container orchestration frameworks.
Debian Taco Cloud Images
The Debian Taco Cloud Images project provide cloud images of Debian Taco for trixie, forky and sid on the amd64, arm64, ppc64el and riscv64 architectures.
Launch and install Debian Taco for your cloud environment!
Debian Taco Live Images
The Debian Taco Live Images project provide live images of Debian Taco for trixie, forky and sid on the amd64 and arm64 architectures.
These images allows running Debian Taco on physical hardware (or virtual machines), and even installation for permanent use.
Debian Taco Build Images and Packages
Packages are built using debdistbuild, which was introduced in a blog about Build Debian in a GitLab Pipeline.
The first step is to prepare build images, which is done by the Debian Taco Build Images project. They are similar to the Debian Taco containers but have build-essential and debdistbuild installed on them.
Debdistbuild is launched in a per-architecture per-suite CI/CD project. Currently only trixie-amd64 is available. That project has built some essential early packages like base-files, debian-archive-keyring and hostname. They are stored in Git LFS backed by a S3 object storage. These packages were all built reproducibly. So this means Debian Taco is still 100% bit-by-bit identical to Debian, except for the renaming.
I’ve yet to launch a more massive wide-scale package rebuild until some outstanding issues have been resolved. I earlier rebuilt around 7000 packages from Trixie on amd64, so I know that the method easily scales.
Remaining work
Where is the diffoscope package outputs and list of package differences? For another holiday! Clearly this is an important remaining work item.
Another important outstanding issue is how to orchestrate launching the build of all packages. Clearly a list of packages is needed, and some trigger mechanism to understand when new packages are added to Debian.
One goal was to build packages from the tag2upload browse.dgit.debian.org archive, before checking the Debian Archive. This ought to be really simple to implement, but other matters came first.
GitLab or Codeberg?
Everything is written using basic POSIX /bin/sh shell scripts. Debian Taco uses the GitLab CI/CD Pipeline mechanism together with a Hetzner S3 object storage to serve packages. The scripts have only weak reliance on GitLab-specific principles, and were designed with the intention to support other platforms. I believe reliance on a particular CI/CD platform is a limitation, so I’d like to explore shipping Debian Taco through a Forgejo-based architecture, possibly via Codeberg as soon as I manage to deploy reliable Forgejo runners.
The important aspects that are required are:
1) Pipelines that can build and publish web sites similar to GitLab Pages. Codeberg has a pipeline mechanism. I’ve successfully used Codeberg Pages to publish the OATH Toolkit homepage homepage. Glueing this together seems feasible.
2) Container Registry. It seems Forgejo supports a Container Registry but I’ve not worked with it at Codeberg to understand if there are any limitations.
3) Package Registry. The Deban Taco live images are uploaded into a package registry, because they are too big for being served through GitLab Pages. It may be converted to using a Pages mechanism, or possibly through Release Artifacts if multi-GB artifacts are supported on other platforms.
I hope to continue this work and explaining more details in a series of posts, stay tuned!